40
VNC 100 DATLNK AUX
1COMPUTER 234PWR USER
KVM Switch
Internet
CAM
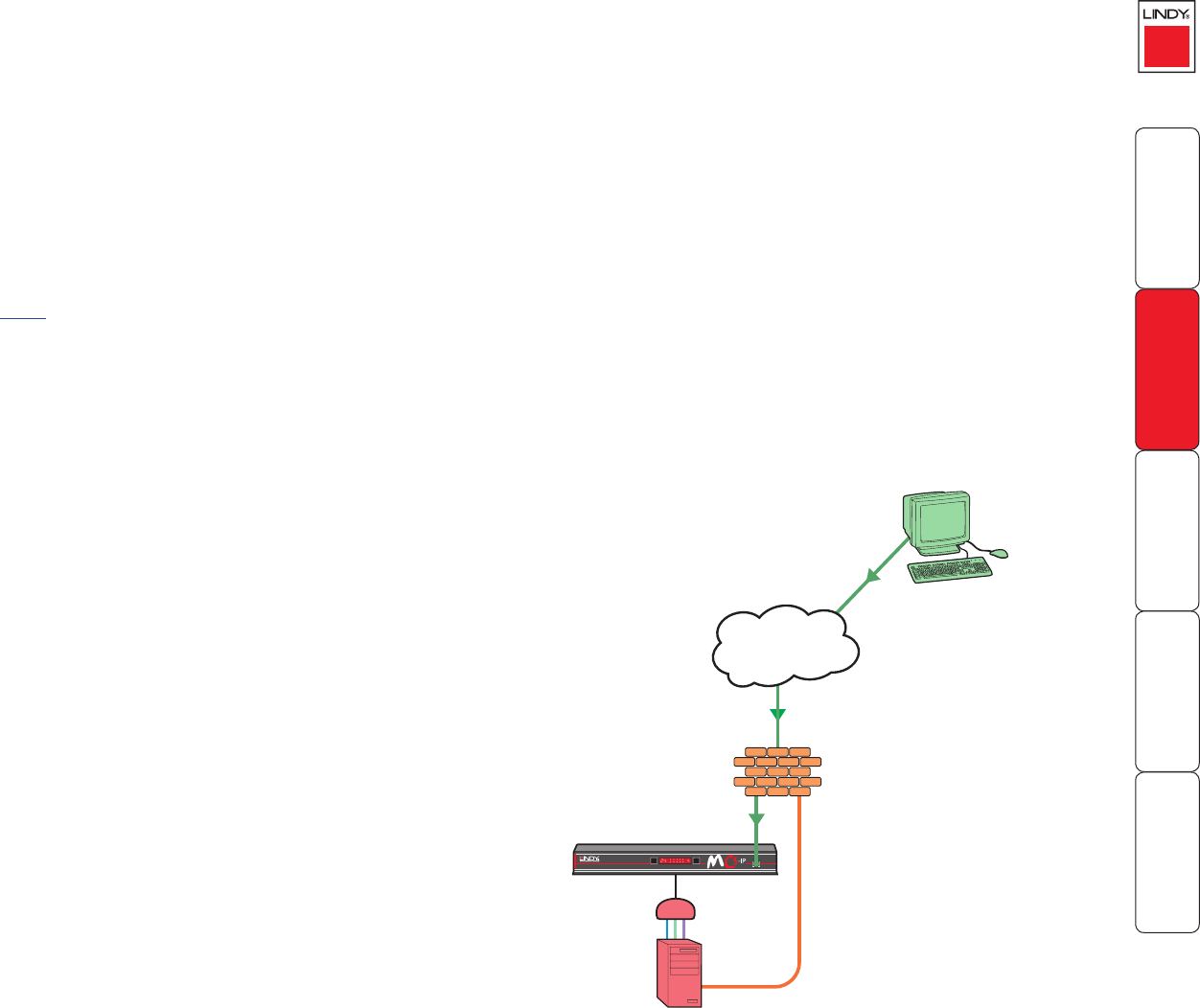
Placing the MC5-IP behind a router or rewall
A possible point of contention between the MC5-IP and a rewall can
occasionally arise over the use of IP ports. Every port through the rewall
represents a potential point of attack from outside and so it is advisable to
minimise the number of open ports. The MC5-IP usually uses two separate port
numbers, however, these are easily changeable and can even be combined into
a single port.
IMPORTANT: The correct conguration of routers and rewalls requires advanced
networking skills and intimate knowledge of the particular network. LINDY
cannot provide specic advice on how to congure your network devices and
strongly recommend that such tasks are carried out by a qualied professional.
Port settings
As standard, the MC5-IP uses two ports to support its two types of viewer:
• Port 80 for users making contact with a web browser, and
• Port 5900 for those using the VNC viewer.
When these port numbers are used, VNC viewers and web browsers will locate
the MC5-IP correctly using only its network address. The rewall/router must be
informed to transfer any trafc requesting these port numbers through to the
MC5-IP.
When a web server is also on the local network
Port 80 is the standard port used by web (HTTP) servers. If the MC5-IP is situated
within a local network that also includes a web server or any other device
serving port 80 then, if you want to use the web browser interface from outside
the local network environment, the HTTP port number of the MC5-IP may need
to be changed.
When you change the HTTP port to anything other than 80, then each remote
browser user will need to specify the port address as well as the IP address. For
instance, if you set the HTTP port to ‘8000’ and the IP address is ‘192.168.47.10’
then browser users will need to enter:
http://192.168.47.10:8000
(Note the single colon that separates the IP address and the port number).
The rewall/router would also need to be informed to transfer all trafc to the
new port number through to the MC5-IP.
If you need to change the VNC port number
If you change the VNC port to anything other than 5900, then each VNC viewer
user will need to specify the port address as well as the IP address. For instance,
if you set the VNC port to ‘11590’ and the IP address is ‘192.168.47.10’ then
VNC viewer users will need to enter:
192.168.47.10::11590
(Note the double colons that separate the IP address and port number).
The rewall/router would also need to be informed to transfer all trafc to the
new port number through to the MC5-IP.
Addressing
When the MC5-IP is situated within the local network, you will need to give
it an appropriate local IP address, IP network mask and default gateway. This
is achieved most easily using the DHCP server option which will apply these
details automatically. If a DHCP server is not available on the network, then
these details need to be applied manually in accordance with the network
administrator.
The rewall/router must then be informed to route incoming requests to port
5900 or port 80 (if available) through to the local address being used by the
MC5-IP.
MC5-IP has a local address
and net mask, i.e.
IP address: 192.168.0.3
Net mask: 255.255.255.0
Remote user with VNC viewer
accesses IP address: 129.7.1.10
and automatically uses port
5900.
Firewall/router address:
129.7.1.10
The rewall routes the
request from the VNC viewer
on port 5900 through to
the MC5-IP at local address
192.168.0.3
