Chapter 4. Tuning the operating system 99
Draft Document for Review May 4, 2007 11:35 am 4285ch04.fm
There is another useful system command, /sbin/service, that enables an administrator to
immediately change the status of any registered service. In a first instance, an administrator
should always choose to check the current status of a service (sendmail in our example) by
issuing this command:
/sbin/service sendmail status
To immediately stop the sendmail daemon in our example, use this command:
/sbin/service sendmail stop
The service command is especially useful to immediately verify whether a daemon is needed,
as changes performed via chkconfig will not be active unless you change the system run level
or perform a reboot. However, a daemon disabled by the service command will be re-enabled
after a reboot. Should the service command not be available with your Linux distribution
there is always the possibility to start or stop a daemon via the init.d directory. Checking the
status of the CUPS daemon for instance could be performed like this:
/etc/init.d/cups status
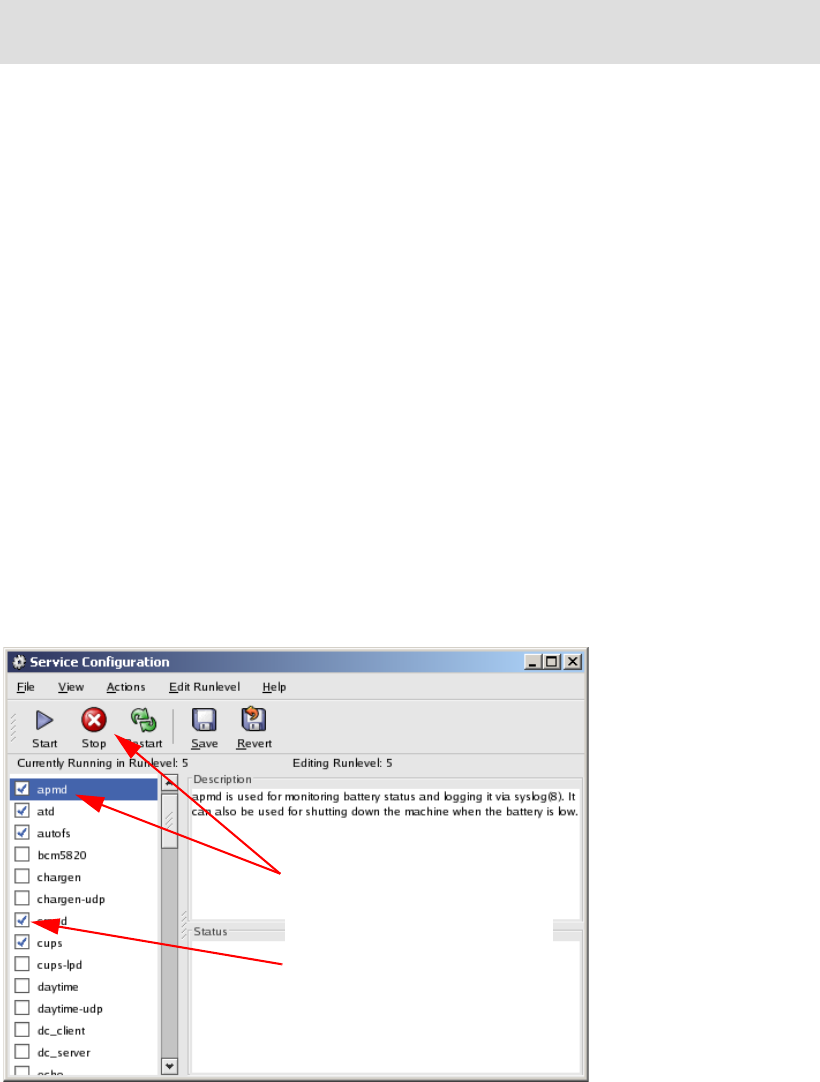
Similarly, there are GUI-based programs for modifying which daemons are started, as shown
in Figure 4-1. To run the service configuration GUI for Red Hat Enterprise Linux, click Main
Menu → System Settings → Server Settings → Services or issue this command:
/usr/bin/redhat-config-services
Figure 4-1 Red Hat Service Configuration interface
Novell SUSE systems offer the same features via the YaST utility. In YaST the service
configuration can be found under System → System Services (Runlevel). Once in the
service configuration we suggest to use the expert mode in order to accurately set the status
of the respective daemon. Running YaST in runlevel 3 would look as shown in Figure 4-2 on
page 100.
Tip: Instead of wasting precious time waiting for a reboot to complete, simply change the
run level to 1 and back to 3 or 5, respectively.
To change the current state,
highlight the daemon and
click Stop.
The check mark indicates the
daemon will start at the next
reboot.
