Chapter 10 Network Address Translation (NAT)
EMG5324-D10A User’s Guide
166
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
10.5 The Address Mapping Screen
Ordering your rules is important because the Device applies the rules in the order that you specify.
When a rule matches the current packet, the Device takes the corresponding action and the
remaining rules are ignored.
Click Network Setting > NAT > Address Mapping to display the following screen.
Figure 76 Network Setting > NAT > Address Mapping
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 43 Network Setting > NAT > Sessions
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAX NAT
Session
Use this field to set a common limit to the number of concurrent NAT sessions each client
computer can have.
If only a few clients use peer to peer applications, you can raise this number to improve
their performance. With heavy peer to peer application use, lower this number to ensure no
single client uses too many of the available NAT sessions.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to restore your previously saved settings.
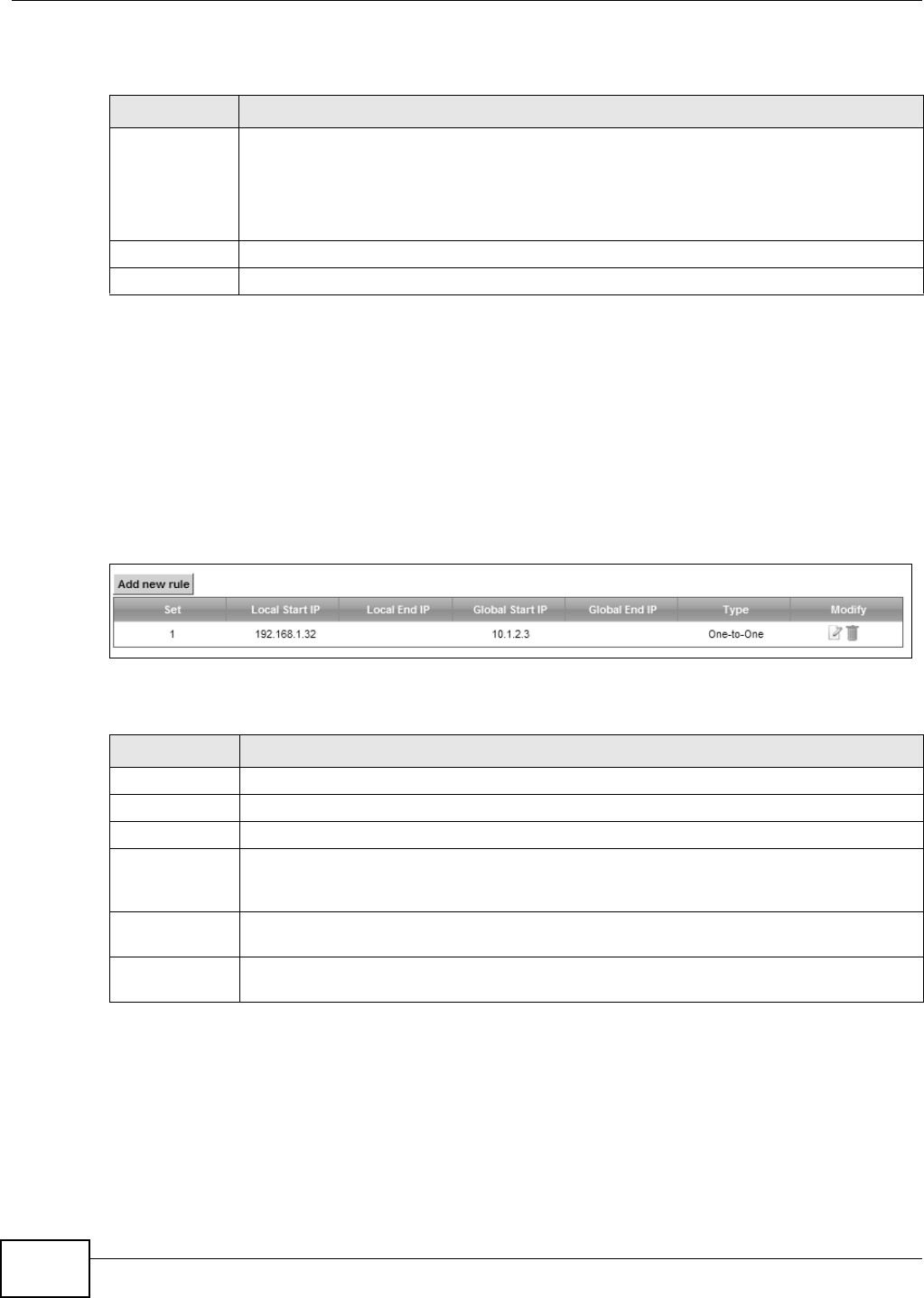
Table 44 Network Setting > NAT > Address Mapping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add new rule Click this to create a new rule.
Set This is the index number of the address mapping set.
Local Start IP This is the starting Inside Local IP Address (ILA).
Local End IP This is the ending Inside Local IP Address (ILA). If the rule is for all local IP addresses, then
this field displays 0.0.0.0 as the Local Start IP address and 255.255.255.255 as the Local
End IP address. This field is blank for One-to-One mapping types.
Global Start IP This is the starting Inside Global IP Address (IGA). Enter 0.0.0.0 here if you have a dynamic
IP address from your ISP. You can only do this for the Many-to-One mapping type.
Global End IP This is the ending Inside Global IP Address (IGA). This field is blank for One-to-One and
Many-to-One mapping types.
