KP915GV Product Manual
107
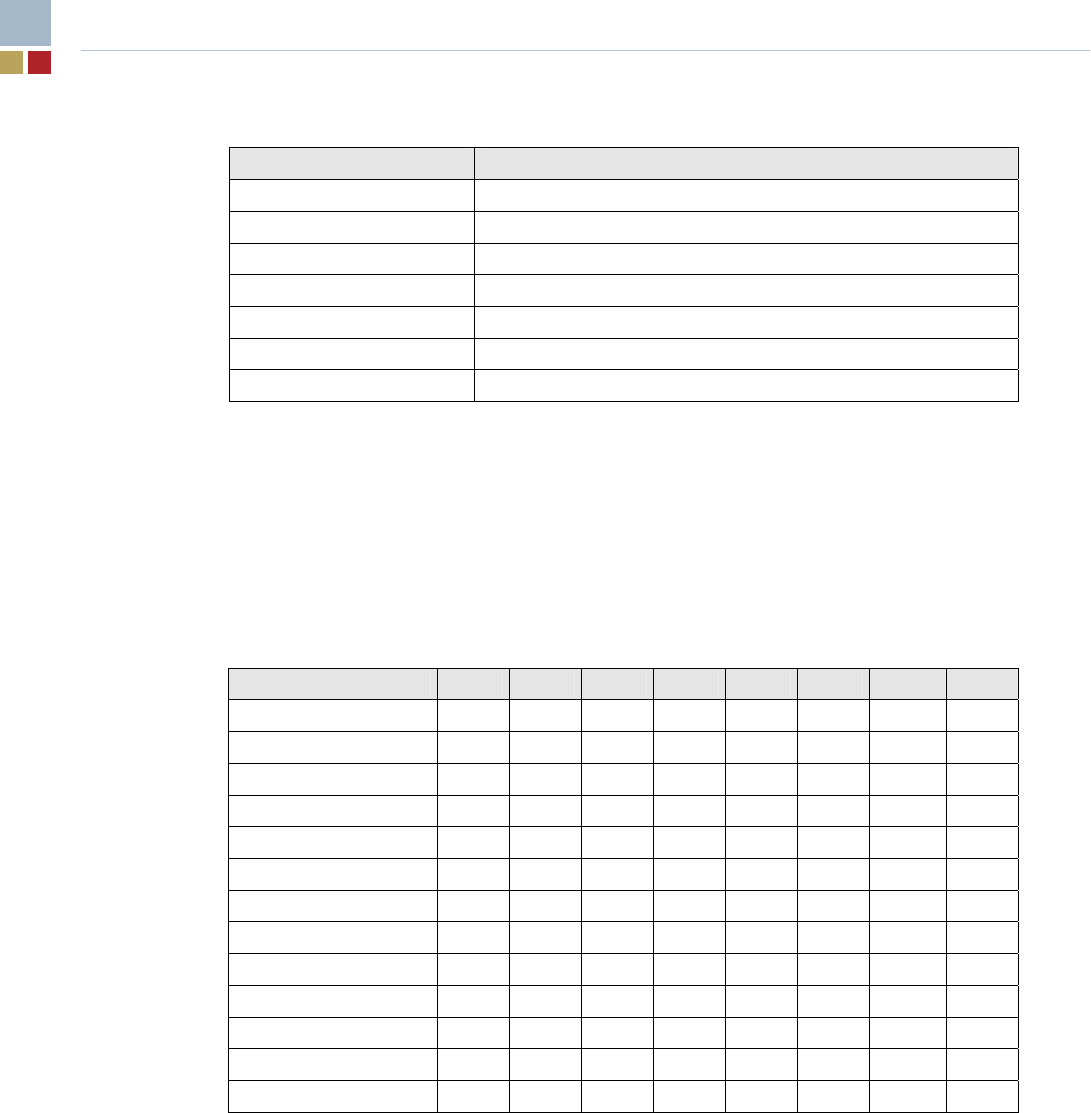
Table 8. I/O Map
Address (hex)* Description
1300 – 133F AC97 audio master
1800 – 182F SIO GPIO and control logic
FFA0 – FFA7 Primary IDE bus master registers
FFA8 – FFAF Secondary IDE bus master registers
Dynamically assigned USB controller (four) (32 locations on 32-byte boundary)
Dynamically assigned SMBus controller (16 locations on 16-byte boundary)
Dynamically assigned LAN controllers (two) (4096 locations on a 4096-byte boundary)
* An ‘x’ prefix for the address indicates that only the low-order 10 address bits are decoded.
A.2 PCI Interrupt Allocation
In order to share PCI interrupts efficiently, the routing of the PCI interrupts INTA - INTD to the
motherboard PCI interrupts PIRQE – PIRQH are rotated for each slot. Thus the PCI card INTA
signals for the PCI slots are spread across these four motherboard inputs. Interrupt routing for the
riser slots is determined by the riser design.
Table 9. PCI Interrupt Allocation
Device PIRQA PIRQB PIRQC PIRQD PIRQE PIRQF PIRQG PIRQH
Slot 1 (AGP4X) INTA INTB – – – – – –
Slot 2 (PCI 2.2) – – – – INTA INTB INTC INTD
Slot 3 (PCI 2.2) – – – – INTD INTA INTB INTC
Slot 4 (PCI 2.2) – – – – INTC INTD INTA INTB
VGA controller INTA – – – – – – –
Ethernet controller 1 INTA – – – – – – –
Ethernet controller 2 – INTA – – – – – –
USB UHCI controller 1 INTA – – – – – – –
USB UHCI controller 2 – – – INTB – – – –
USB UHCI controller 3 – – INTC – – – – –
USB EHCI controller – – – – – – – INTD
SMBus controller – INTB – – – – – –
AC97 controller – INTB – – – – – –
Example. From the previous table, the INTA interrupt from a card plugged into slot 2 would be
routed to the motherboard PIRQE.
